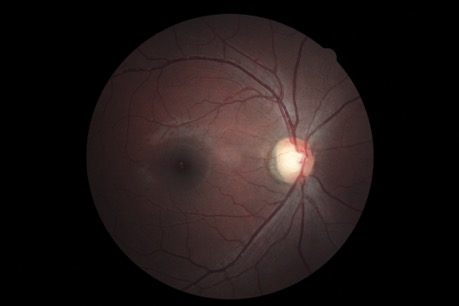
What is Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)?
Diabetic retinopathy is a major ocular complication of diabetes mellitus in which excess glucose in the bloodstream causes damage to the blood vessels of the retina. It is the leading cause of blindness among working age adults in the US (adults between the ages of 20 and 74 years). Between 2005 and 2008, 4.2 million or 28.5% of people with diabetes aged 40 years or older had diabetic retinopathy. Laser photocoagulation surgery is an effective way of treating diabetic retinopathy, if it is detected early.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine learning involves the use of mathematics and statistical theory to create models that capture existing patterns in example data or from past experience in order to utilize these patterns to solve new problems. As different models exhibit different biases, we have employed several modeling approaches that are the focus of active research in the computer science domain; and on the same training examples to determine which set of assumptions best suit the data.
Screening Recommendations
Annual retinal screening has been recommended as a means of detecting diabetic retinopathy and potentially reducing the incidence of blindness due to this condition. Studies focused on the urban safety net setting have shown annual eye examination rates for inner-city diabetic patients to be lower than 25% while the national average is 60%. Teleretinal screenings may be of benefit in urban safety net settings, since several studies have demonstrated that inner-city patients with diabetes also have limited access to specialty eye care and that this is tied to delayed diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy.
Since 1993
Purpose
The present study aims to build upon prior research by: (a) developing novel software that utilizes information from clinical records to detect latent diabetic retinopathy in diabetic patients who have not yet received an annual eye examination, and (b) devising methods to speed up the diabetic retinopathy detection process for diabetic patients who have had digital retinal images taken by partially automating the process using image processing and machine learning techniques.